Intro
比赛地址https://ctf.xidian.edu.cn/
很棒的新生赛,去年这个时候还看不懂题,今年成功akCrypto了 大致本文就密码方向的题来进行一个Write的Up
Challenge
密码学入门指北
ElGamal非对称 给你了私钥 如下计算
exp
1 | p = |
ez_DES
1 | from Crypto.Cipher import DES |
DES作为一组对称的分组密码 使用相同的密钥进行加密解密 密钥组成是”ezdes???“我们直接穷举爆破密钥即可
exp
1 | from Crypto.Cipher import DES |
实际上多个不同的key都能解出一样的flag
baby-next
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, inverse |
ezBSGS
即求解DLP
1 | a = 13 |
说回BSGS算法本身 是一种用空间换时间的搜索策略
对于生成元为
我们有
ez_square
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
我们需要解形似
方法比较多 我们来讲几个经典的
首先我们的RSA解密加密都是在模
其余方法如下
sagemath里面有这种判断并且恢复two_squares(),源码大致如下
1 | cdef int two_squares_c(uint_fast32_t n, uint_fast32_t res[2]) noexcept: |
大致思路是任何形如
同时还存在一种复数域下的因数分解
还想到另一种在高斯整数环(复数域)下的分解
1 | n = 83917281059209836833837824007690691544699901753577294450739161840987816051781770716778159151802639720854808886223999296102766845876403271538287419091422744267873129896312388567406645946985868002735024896571899580581985438021613509956651683237014111116217116870686535030557076307205101926450610365611263289149 |
直接造方程也可以 这里是简单搜索出
ez_AES
1 | from secret import flag |
简化后的AES对称 直接交给GPT梭了
exp
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
ez_det
1 | from random import randrange |
给出的明文矩阵形似
给出密文矩阵
Step 1: 利用后 4 列恢复 ( A ) 的前 4 列
观察 ( M ) 的后 4 列(列 1~4,索引从 0 开始): - 第 5 行全为 0 -
所以前 4 行构成了一个 4×4 子矩阵
设:
由于
但由于
因此,后 4 列的乘法实际上只涉及
令
于是可解:
Step 2: 利用第一列关系提取含
现在看
移项得:
Step 3: 构造矩阵
现在构造新矩阵:
而题目中 make_mask 保证了:
1 |
|
ezlegendre
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import getPrime, bytes_to_long |
和去年的一样 利用二次剩余逐比特恢复即可
当
exp
1 |
|
ChallengeMore
杂交随机数
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long |
杂糅lcg与lfsr的prng,我们梳理一下逻辑
L
R两个块
m是一个掩码位,b是参数
给lcg用的,随后用R对L进行LFSR处理,R自身进行一个LCG,seed是原本的L,随后交换LR,最后告诉你末态
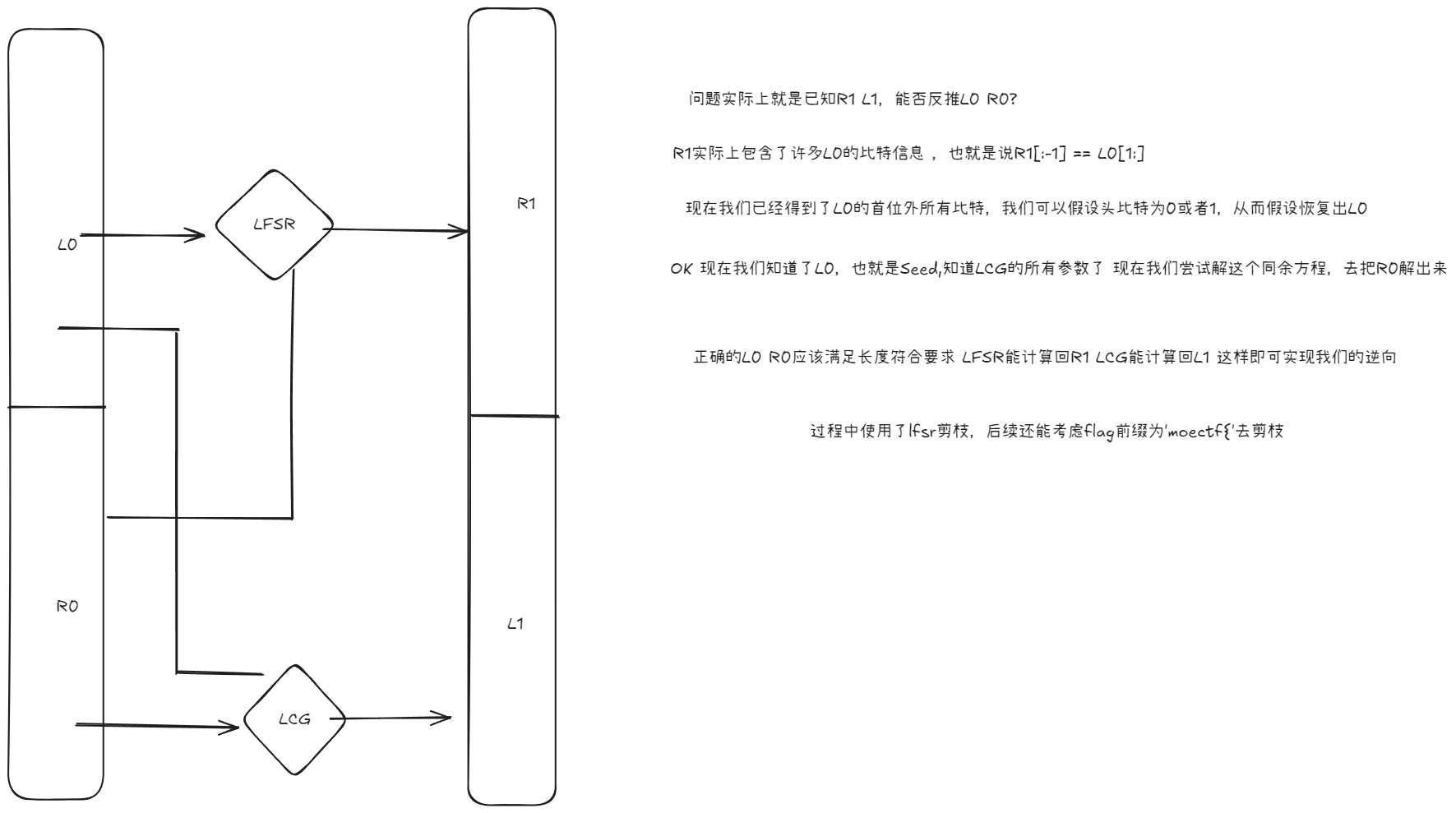
DFS剪枝的脚本by GPT5老师
1 | # Using prefix pruning: Deepening the bounded DFS and random trials with known prefix 'moectf{'. |
sandtea姐姐的fufu
背包问题 让GPT老师梭了 就不放exp了()
半^3部电台
1 | from random import choice |
一个对称问题,类似魔改的DES加密Fesitel网格,块加密的思路为
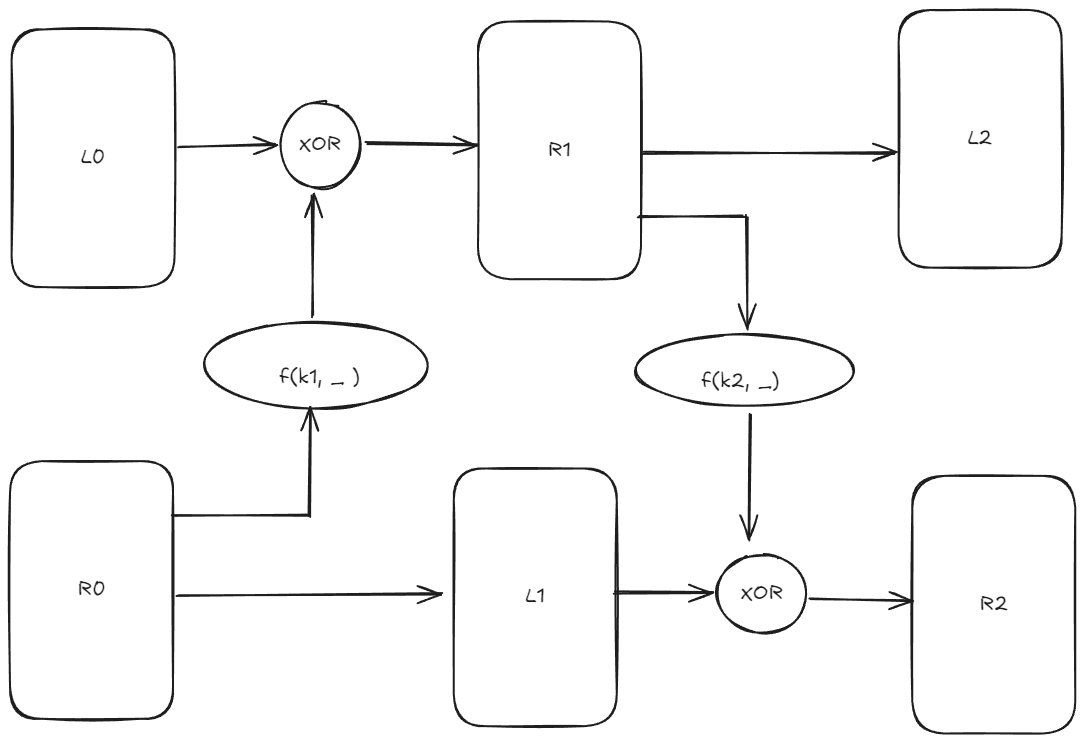
我们能得到
DES的轮函数是
在DES中我们的操作
对于已知的
这里的关键点就是二轮Fesitel网络的安全性太低 我们可以通过简单的推导从已知的明文块密文块泄露大部分有关密钥的信息
同样的,exp by GPT5老师
1 | # We'll reconstruct the 2-round DES-like cipher, recover K1 and K2 from the provided |
简单分析输出后得到flagmoectf{1eEkSN!y3}
Ez_wiener
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import* |
基于连分数的Wiener攻击,思路如下
当
Legendre's theorem
如果存在
我们称
故这里,我们想想,在RSA中
我们来算一下
而
所以
思路明确了,在这种情况下我们计算
得到若干组可能的
exp
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
prime-in-prime
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, bytes_to_long, getPrime |
我们有
我们考虑
如果有
exp
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
貌似是RSA Common Prime Attack
ez_lattice
1 | from random import randrange |
矩阵运算的左乘不会影响格基的线性关系
我们的flag总是保持是最优的这个线性组合
,题目相当于对flag矩阵进行线性组合得到C,而我们的基却直接是
exp
1 | p= |
happyRSA
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import getPrime, bytes_to_long |
尝试有
其中我们的
我们先考虑对(1)来展开,超过3次幂的都会被约去,也就是
显然有
我们又已经有
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
ezhalf_gcd
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, getStrongPrime |
给了你
考虑恢复出我们的
我们已知
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
解方程
1 | k1 = 13956969191637195871632957505406117751565360403440829727249072761352047425739750866240599441725739309449282190348085360109677584507525554127026445196148893160857286022203801997873156811960571737271597472086993749971283966198697191943628862781066725335706690253538900770669084526246573003464456817905257894602490888900824860753149136591999728629106864099281400347411046856634802687971218504308172469580264497048520451583896989424545232463140527591539153615957817302334587761071546151380508318892302985208301605902883263311183702458763989755391843198670020891760809561155674454979493217081297358303315754142647867287413 |
神秘数字太多了
转化为带
即
1 | p = 10000000000099 |
wiener++
三元ExtendWienerAttack 直接梭别的师傅的板子
1 | E = |
湾区杯2025出过一道非常诡异的
ledengre_revenge
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
系统比较繁,整理一下就是
part1.
给出32字节的flag,两个字节两个字节的切片,切出16块放到一个p_的勒让德符号,如果是二次剩余,代表1,不是二次剩余,代表0,最终拼起来得到一个16位的key,由这个key构造AES加密器,同时还给出了
把flag拆成左右各16字节两个块,作为text数组的初始值,
随后的操作进行10轮
对块中16字节进行加密后得到enc密文,拆成16份放到4*4矩阵中,构造出matrix, 每份1字节,同时我们定义一个标记矩阵lis用来记录我们比较的结果,
对于加密矩阵matrix中的每一个值,和给定的矩阵a进行一个比较,如果满足给定的大小关系,我们就给lis标记矩阵的这一个元素的这一位是1,否则是0
最后对每个元素,我们丢入function,构造出一个处理后的矩阵matrix,
最后给你的是两轮比较的结果lis 以及初始的a矩阵 两端text的计算处理结果
信息很多 很杂 我们来分析一下我们有什么
e
p ,也就是
functionp_
flag的长度
用于比较的标准矩阵a
两轮比较结果lis
密文处理结果text
我们先尝试能不能通过离散对数求出p_ - 1很光滑,还已知key的范围是
1 | p_ = 71583805456773770888820224577418671344500223401233301642692926000191389937709 |
求出来key后 我们有两点突破,首先是AES加密器相当于白盒了,其次我们会看key的生成过程,看看能不能推导出原本flag的某些信息
我们看向key的生成过程
1 | text_=[[pow(bytes_to_long(flag[(row+col*4)*2:(row+col*4)*2+2]),-2,p_)+1 for row in range(4)] for col in range(4)] |
把flag拆成16个块,每个块2字节,对于每两个字节的块 ,我们可以去算它的text,也就是
1 | f_i = bytes_to_long(flag_block_i) |
然后key在这一位的比特说明了text_i对p_是否是二次剩余,我们很难逆向求flag
但是保留了验证flag的一个思路
随后我们分析后面的比较以及矩阵构造的过程,key已知 ,而且注意到这里的AES是ECB模式,也就是说flag的块与块之间的加密是互不干扰的,加上我们已知了
flag第一个块是moectf{?????????,此时爆破就具备一定可行性了,接着往下看,lis实际就是flag放进去验证的过程
,但是实际中我们组合的时候满足条件的二次剩余&二次非剩余的取值还是太多
不能爆破
而且上述做法实际上没有用到题目给定的text ,于是还是尝试从终态的text结构逆向来求解这个问题
最关键的点在于函数function是否可逆?
题目给我们的素数p=251实际上满足
当
首先根据最终的text还原我们末态的text状态
1 | text = P(text) |
接着 我们逆向function函数
1 | def inv_function(x,p): |
接下来只需要从终态出发,逆着走一遍过程即可,让G老师结合已有信息写了个脚本
1 | # solve.py |
End
时间过的好快啊 做题的时候似乎去年那个刚刚接触CTF,接触CS的自己就在眼前,页面还是一样的 机子还是一样的 已经从下不了手逐渐到现在的ak Crypto/Reverse了,或许从单纯的加分来说,CTF的获奖难度不算是什么很有”性价比”去值得做的事情吧,但是单纯享受密码学的优雅,享受用严谨的数学推导追根溯源的过程,有时候生活,学习不就是这些简单的正反馈支撑着我们一路走来嘛
Moe年年都在办 师傅们也是一轮一轮的换代 成长 DAWN2025的新生力量们非常强 这次合力打下了rk3 加油啊
一年能让人成长很多,期待下一个一年,祝moe和西电Sec越办越好!我们明年再见!